PHP 7
(Dezember 2015)
Alle Änderungen im Überblick
Geschwindigkeit
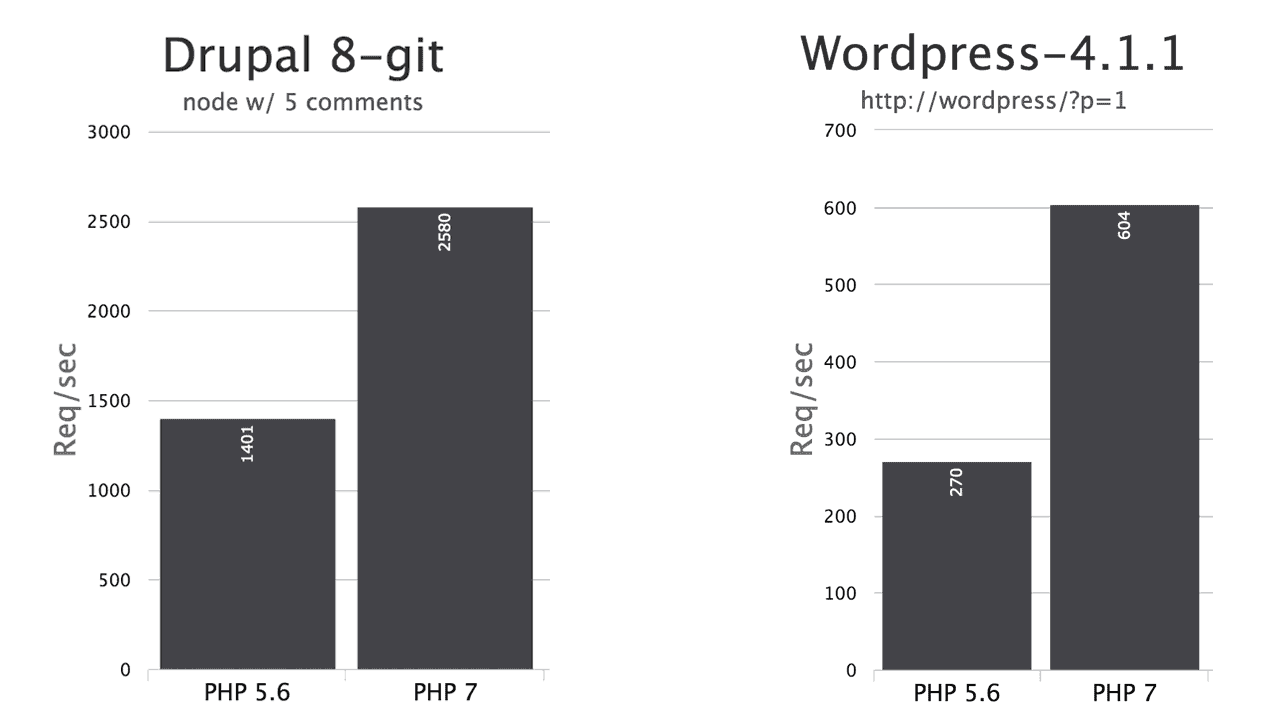 Quelle: 5 New Features in PHP 7
Quelle: 5 New Features in PHP 7
Fehlerbehandlung
ThrowableErrorTypeErrorParseErrorAssertionErrorArithmeticErrorDivisionByZeroError
Nicht kompatible Änderungen (Quelle)
set_exception_handler()- Erhält nicht mehrException-ObjektExceptionbeim fehlerhaften Konstruktor in internen Klassen (früherNULL)Parser errorwirft einParseError-Objekt-
E_STRICT-Meldunge wurden auf andere Level verlegt - Verarbeitung von "indirekten" Variablen, Eigenschaften und Methoden
-
list()-
Die Reihenfolge, in der die Zuweisungsoperationen durchgeführt werden, wurde geändert
list($a[], $a[], $a[]) = [1, 2, 3]; var_dump($a); - Ausdrücke dürfen nicht mehr vollständig leer sein
-
Zeichenketten können nicht mehr entpackt werden
$string = "abcde"; list($foo) = $string; var_dump($foo); // string(1) "a"
-
Die Reihenfolge, in der die Zuweisungsoperationen durchgeführt werden, wurde geändert
-
foreachändert nicht mehr den internen Array-Zeiger$array = [0, 1, 2]; foreach ($array as &$val) { var_dump(current($array)); } // PHP 5 int(1) int(2) bool(false) // PHP 7 int(0) int(0) int(0)
-
foreach- Geändertes Verhalten bei Referenzen$array = [0]; foreach ($array as &$val) { var_dump($val); $array[1] = 1; } // PHP 5 int(0) // PHP 7 int(0) int(1)
Entfernte Funktionen
call_user_method()undcall_user_method_array()mcrypt_generic_end()datefmt_set_timezone_id()undIntlDateFormatter::setTimeZoneID()set_magic_quotes_runtime()undmagic_quotes_runtime()imagepsbbox(),imagepsencodefont(),imagepsextendfont(),imagepsfreefont(),imagepsloadfont(),imagepsslantfont(),imagepstext()
Unzulässige Namen für Klassen, Interfaces und Traits
- bool, int, float, string, NULL, TRUE, FALSE
- resource, object, mixed, numeric
ASP entfernt
<% %><%= %>
Neue Features (Quelle)
-
Scalar type declarations
function sum(int $a, int $b) { return $a + $b; } var_dump(sum(1, 2)); // 3 var_dump(sum(1.5, 2.5)); // 3declare(strict_types=1); function sum(int $a, int $b) { return $a + $b; } var_dump(sum(1, 2)); // 3 var_dump(sum(1, 2.5)); Fatal error: Uncaught TypeError: Argument 2 passed to sum() must be of the type int, float given
-
Return type declarations
function sum(int $a, int $b): int { return $a + $b; } var_dump(sum(1, 2)); // 3 var_dump(sum(1.5, 2.5)); // 3declare(strict_types=1); function sum(int $a, int $b): int { return $a + $b; } var_dump(sum(1, 2)); // 3 var_dump(sum(1.5, 2.5)); // Fatal error: Uncaught TypeError: Return value of sum() must be of the type integer, float returned
-
Null coalescing operator
// PHP < 7 $username = isset($_GET['user']) ? $_GET['user'] : 'nobody'; // PHP 7 $username = $_GET['user'] ?? 'nobody'; $username = $_GET['user'] ?? $_POST['user'] ?? 'nobody';
-
Spaceship operator
// Integers echo 1 <=> 1; // 0 echo 1 <=> 2; // -1 echo 2 <=> 1; // 1 // Floats echo 1.5 <=> 1.5; // 0 echo 1.5 <=> 2.5; // -1 echo 2.5 <=> 1.5; // 1 // Strings echo "a" <=> "a"; // 0 echo "a" <=> "b"; // -1 echo "b" <=> "a"; // 1
- Arrays in Konstanten
- Anonyme Klassen
-
Filtered unserialize()
// converts all objects into __PHP_Incomplete_Class object $data = unserialize($foo, ["allowed_classes" => false]); // converts all objects into __PHP_Incomplete_Class object except those of MyClass and MyClass2 $data = unserialize($foo, ["allowed_classes" => ["MyClass", "MyClass2"]]); // default behaviour (same as omitting the second argument) that accepts all classes $data = unserialize($foo, ["allowed_classes" => true]);
-
Guppierte
useDeclarationen// PHP 7+ code use some\namespace\{ClassA, ClassB, ClassC as C}; use function some\namespace\{fn_a, fn_b, fn_c}; use const some\namespace\{ConstA, ConstB, ConstC}; - Session-Optionen (Array mit "session configuration directives")
Veraltet (Quelle)
- Konstruktoren aus PHP 4
- Statischer Aufruf von nicht statischen Methoden
- Salt-Option in
password_hash()entfernt
Geänderte Funktionen (Quelle)
dirname()- Neuer Parameterlevelspreg_replace()- \e entfernt (Achtung Symfony 1.*!)- und andere
Neue Funktionen (Quelle)
random_bytes()random_int()error_clear_last()intdiv()preg_replace_callback_array()- und andere
Neue Klassen (Quelle)
ReflectionGeneratorReflectionTypeIntlChar
Entfernte Erweiterungen (Quelle)
- ereg
- mssql
- mysql
- sybase_ct